The Hidden Language and Secrets of Lost Civilizations!
Are you curious about the meaning behind ancient scripts? Have you ever wondered how they influence modern language, art, or even that tattoo you’re considering?
This article unveils the intriguing world of ancient scripts, from hieroglyphics to Mayan Glyphs. It presents an insightful overview of their history, significance, and global variations.
This article gives you a fresh perspective on the roots of written communication and its pervasive influence on our contemporary world.
So, don’t stop here. Continue reading to unlock the concealed knowledge of ancient scripts.
Let’s get started!

Here’s What You Will Find

Key Takeaways
Ancient Scripts
The Role of Ancient Scripts: Ancient scripts such as Hieroglyphic, Cuneiform, and Greek are physical evidence of human cognition, faith, and historical happenings.
Cultural Reflection of Ancient Scripts: These scripts mirror the multicultural essence of ancient societies, demonstrating cultural amalgamation and interconnection.
Classification of Ancient Scripts: Ancient scripts can be classified into three categories: ideographic, syllabic, and alphabetic scripts, each displaying its distinct traits and applications.
Decoding Ancient Scripts: To make sense of ancient scripts, one must understand the cultural backdrop, as they visually express sophisticated ideas, spiritual rituals, and philosophical concepts.
What are Ancient Scripts?
Definition of ancient scripts as systems of writing used in early civilizations.
Ancient scripts are writing systems developed by early civilizations to document language and communicate. They range from pictographic and ideographic symbols representing objects or ideas to phonetic writing recording speech sounds.
Ancient scripts were used for various purposes, including recording historical events, religious texts, legal codes, and commercial transactions.
They are fundamental to understanding human history, offering insights into ancient societies’ culture, beliefs, and daily life. Examples include Egyptian hieroglyphs, Mesopotamian cuneiform, Chinese characters, and the Mayan script, each uniquely contributing to the legacy of human communication and civilization.
Ancient scripts are intricate writing systems developed by early civilizations for recording and communicating information. These scripts are foundational to understanding historical interactions and cultural developments.
Each script, symbol, or character offers a unique glimpse into our ancestors’ lives, beliefs, and societies, serving as a direct link to understanding our shared human history.
Did You Know?
Ancient writings provide insights into social hierarchies, political structures, religious beliefs, economic activities, and technological advancements of their times.
Engaging with these scripts is not merely an academic pursuit but an exploration into the depth of human civilization, offering a vivid experience of the past. They narrate the silent stories of our ancestors, making ancient scripts a treasure trove of knowledge and a testament to human ingenuity and expression throughout history.
Other Names
You might be familiar with terms like hieroglyphics and cuneiform, but did you know these are just a couple of the many other names for ancient scripts? Each name is often tied to a particular culture and period, painting a vibrant picture of our global history.
Let’s explore these alternative terms and the cultures they’re associated with to broaden our understanding of ancient scripts.
- Egyptian Hieroglyphs
- Cuneiform
- Mayan Glyphs
- Phoenician Alphabet
- Brahmi Script
- Linear B
- Ogham
This list showcases the diversity and rich heritage of ancient scripts, each carrying its unique legacy across time and culture.
Types of Ancient Scripts
Unraveling Historical Linguistics
The fascinating journey of human communication through writing reveals a complex tapestry of ancient scripts, each with its unique structure, purpose, and geographical origins.
These scripts, developed over millennia, served as the cornerstone for recording history, laws, literature, and the mundane details of daily life. The evolution of writing systems reflects the ingenuity and adaptability of ancient civilizations in their quest to document the world around them.
Logographic Scripts
Logographic scripts represent words or morphemes (the smallest meaningful units in a language) as symbols or characters. Each symbol represents a word or a significant concept, often requiring learners to recognize thousands of different characters.
- Chinese Characters: The most renowned logographic system, Chinese characters have been used to write various languages across East Asia. Each character represents a word or a morpheme, with over 50,000 characters, though a few thousand are commonly used.
- Cuneiform: Originating in ancient Mesopotamia, cuneiform script includes a mix of logographic and syllabic elements. It evolved from pictographs and was used by various cultures, including the Sumerians and Akkadians.
- Egyptian Hieroglyphs: These iconic logograms, blending logographic and alphabetic elements, were used by ancient Egyptians. They adorned temples, tombs, and papyri and served religious, administrative, and literary purposes.
Syllabic Scripts
Syllabic scripts represent language sounds at the syllable level, each symbol for a consonant-vowel combination or a standalone vowel.
- Linear B: An ancient script used in Mycenaean Greece, Linear B is a syllabic script deciphered in the 20th century. It reveals insights into the early Greek language and Mycenaean administration.
- Cuneiform Syllabaries: Beyond its logographic use, cuneiform also developed syllabic forms used by the Akkadians, Babylonians, and Assyrians, showcasing its versatility across languages and time.
Alphabetic Scripts
Alphabetic scripts are based on representing individual sounds of a language, making them more straightforward to learn than logographic systems.
- Phoenician Alphabet: The Phoenician alphabet, primarily consonantal, is considered the ancestor of many modern alphabets. It influenced the development of the Greek, Hebrew, and Latin alphabets.
- Greek Alphabet: The Greek alphabet, derived from the Phoenician script, added vowels, laying the groundwork for the alphabetic systems used in many languages today.
Pictographic Scripts
Pictographic scripts use simple drawings or symbols to represent objects or concepts. These scripts are the precursors to more complex writing systems.
- Petroglyphs and Rock Art: Found worldwide, these ancient markings on rocks and caves represent early human attempts to record their experiences and beliefs visually.
Abugida Scripts
Abugida scripts, also known as alphasyllabaries, represent consonants with inherent vowel sounds that can be altered with diacritics.
- Brahmi Script: An ancient Indian script, Brahmi is the forebear of many South and Southeast Asian scripts. It marks consonants with an inherent ‘a’ sound, modified by diacritics for other vowels.
- Ge’ez Script: Used in Ethiopia and Eritrea, the Ge’ez script is an abugida adapted for several languages, including Amharic and Tigrinya.
Abjads (Consonantal Alphabets)
Abjads are scripts primarily recording consonants, leaving most vowels unspecified, a characteristic found in several Semitic languages.
- Arabic Script: Widely used across the Muslim world, the Arabic script is an abjad adapted for numerous languages, including Persian, Urdu, and Pashto.
- Hebrew Script: The Hebrew script is another example used for the Hebrew language and Jewish liturgy, retaining a core set of consonantal symbols while indicating vowels optionally.
Undeciphered Scripts
These scripts remain a mystery, and their languages and meanings are not yet fully understood. They represent some of the most intriguing puzzles in linguistics and archaeology.
- Indus Script: Associated with the ancient Indus Valley Civilization, this script’s language and content remain undeciphered, limiting our understanding of this advanced culture.
- Linear A: Predating Linear B, Linear A was used by the Minoans of Crete and, unlike its successor, has not been deciphered, leaving a gap in our knowledge of Minoan society and language.
Each ancient script serves as a window into the minds and lives of our ancestors, offering invaluable insights into the development of human thought, culture, and civilization.
Studying these scripts uncovers the roots of written communication and fosters a deeper appreciation for the complexity and diversity of human languages throughout history.
Comparative Overview of Ancient Scripts
Origins, Symbolism, and Modern Influence
| Ancient Script | Alternate Names | Time Frame | Description | Example Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Egyptian Hieroglyphs | Sacred Script, Medu Neter | c. 3200 BCE – 400 CE | One of the earliest writing systems, developed in Sumer, was used for various languages and purposes across Mesopotamia. | In early medieval Britain and Ireland, an alphabet consisting of strokes and notches carved on stones, primarily for memorials or boundary markers, was used. |
| Cuneiform | Wedge Script, Assyrian Script | c. 3400 BCE – 1st century CE | Administrative records, legal documents, and literature. | An alphabet consisting of strokes and notches carved on stones, primarily for memorials or boundary markers, was used in early medieval Britain and Ireland. |
| Mayan Glyphs | Maya Script, Maya Hieroglyphs | c. 3rd century BCE – 16th century CE | One of the earliest writing systems, developed in Sumer, was used for various languages and purposes across Mesopotamia. | Codices, stelae, pottery, and architecture. |
| Phoenician Alphabet | Canaanite Script, Proto-Canaanite Alphabet | c. 1050 BCE – 300 BCE | A consonantal alphabet that simplified previous writing systems, facilitating the spread of knowledge and culture across the Mediterranean. | Inscriptions on stone monuments and pottery. |
| Brahmi Script | Brahmi, Asokan Script | c. 3rd century BCE – 5th century CE | The ancestor of many South and Southeast Asian scripts, used extensively for Buddhist and Hindu texts. | Religious texts, inscriptions on pillars and caves. |
| Linear B | Mycenaean Script, Minoan Linear B | c. 1450 BCE – 1200 BCE | Used by the Mycenaean Greeks for administrative purposes, revealing details about their society, economy, and religion. | Tablets detailing inventory lists and transactions. |
| Ogham | Celtic Tree Alphabet, Ogam | c. 4th century CE – 9th century CE | An alphabet used in early medieval Britain and Ireland, consisting of strokes and notches carved on stones, primarily for memorials or boundary markers. | Standing stones, memorial inscriptions. |
Ancient Scripts Examples
A Glimpse into the Past
The world of ancient scripts is as vast as it is fascinating. They offer a unique lens through which we can view our ancestors’ cultures, ideologies, and innovations.
These scripts served as practical tools for communication and record-keeping and as profound expressions of artistic and intellectual achievement.
Egyptian Hieroglyphs:
The Language of the Gods
Egyptian hieroglyphs, one of the oldest writing systems in the world, were used in Egypt for over 3,000 years. This script combined logographic, syllabic, and alphabetic elements, allowing for a versatile expression of the Egyptian language.

Hieroglyphs were considered sacred and used in religious texts and monumental inscriptions. Perhaps best exemplified are the inscriptions found within the tombs of Pharaohs, such as those in the Valley of the Kings, where they were intended to guide the deceased through the afterlife.
Cuneiform
The Clay Tablets of Mesopotamia
Cuneiform script originated around 3400 BCE in Sumer (modern-day Iraq) and is one of humanity’s earliest writing systems. Initially pictographic, it evolved into a complex system of wedge-shaped marks pressed into clay tablets.
Cuneiform was used for various languages and purposes, including administration, trade, literature, and law. The Epic of Gilgamesh, one of the oldest known works of literature, was written in Akkadian cuneiform.
Mayan Glyphs
The Mysterious Mesoamerican Code
The Mayan script, also known as Mayan glyphs, was the writing system of the Maya civilization of Mesoamerica and is notable for its complexity and beauty. It combines logograms and syllabic signs used extensively from the 3rd century BCE to the 16th century CE.
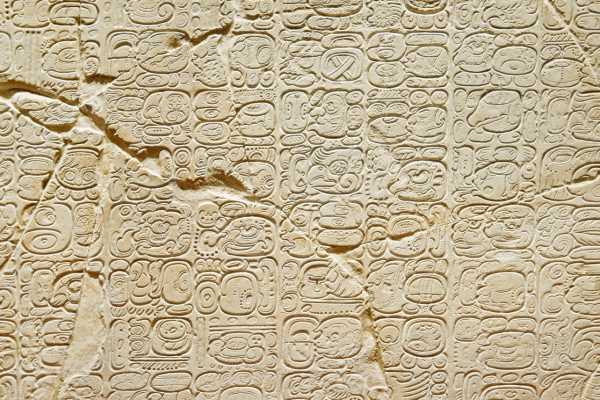

The Maya recorded their history and knowledge of astronomy, mathematics, and theology in codices and on monuments. The decipherment of Mayan glyphs in the 20th century opened a window into Mayan history and culture, highlighting their sophisticated understanding of time and cosmology.
The Phoenician Alphabet
The Seed of Modern Writing
The Phoenician alphabet, developed around 1050 BCE, is recognized for its significant influence on the development of alphabetic writing systems worldwide.
Originating in the region of modern-day Lebanon, the consonantal alphabet (or abjad) simplified previous writing systems, making them more accessible and easier to learn.
The Phoenician traders and sailors spread their alphabet across the Mediterranean, which inspired the Greek and Latin alphabets, among others. This script played a crucial role in the evolution of written communication, paving the way for the alphabets used in many of today’s languages.
Brahmi
The Ancestor of Indian Scripts
Brahmi is considered the ancestor of a diverse family of scripts across South and Southeast Asia. Emerging around the 3rd century BCE, it recorded religious texts, inscriptions, and administrative documents that were pivotal in spreading Buddhism and Hinduism.
The Ashokan edicts, inscribed on pillars and rocks across the Indian subcontinent, are among the oldest known Brahmi inscriptions, showcasing the script’s role in disseminating Emperor Ashoka’s teachings.
Linear B
Deciphering the Mycenaean World
Linear B, deciphered in the mid-20th century by Michael Ventris, is an ancient script used by the Mycenaean Greeks from about 1450 to 1200 BCE. It was primarily used for administrative and accounting purposes, with tablets recording inventory lists, transactions, and offerings to deities. The discovery and decipherment of Linear B tablets, particularly at the site of Pylos, provided invaluable insights into the economic organization, social structure, and religious practices of late Bronze Age Greek societies.
Ogham
The Celtic Mystery
Ogham is an ancient alphabet used primarily in Ireland and parts of Wales, Scotland, and England from the 4th to the 9th centuries CE. Comprising a series of strokes and notches carved along the edge of standing stones, Ogham inscriptions are primarily memorials or boundary markers.
Ogham’s precise purpose and origins remain controversial, but its existence underscores the rich tapestry of writing systems developed across ancient Europe.
Each of these examples underscores the diversity and complexity of ancient scripts, reflecting the wide array of methods our ancestors developed to record their languages and cultures. Studying these scripts is not just an academic pursuit but a journey into the heart of human civilization, revealing the universal desire to communicate, commemorate, and understand the world.
What is the Oldest Written Script?
The title of the oldest written script is often attributed to cuneiform, developed by the Sumerians of ancient Mesopotamia around 3400 BC to 3200 BC.
Cuneiform began as a system of pictographs and evolved into a complex script used for various purposes, including administration, trade, literature, and law.
This script was written by pressing a reed stylus into clay tablets, creating wedge-shaped marks. The discovery and decipherment of cuneiform texts have provided invaluable insights into ancient Mesopotamian civilization, its culture, economy, and history.
Difference Between Scripts and Spoken Language
The distinction between ancient scripts and spoken languages is pivotal for understanding human history and communication.
Scripts are systems of visual symbols used to represent language in written form, whereas spoken language is the auditory and often gestural means by which humans communicate orally.
While ancient scripts are enduring records of civilizations, documenting historical events, religious practices, and complex ideas, they are not simply written versions of spoken languages.
They represent a broader communication system, often encapsulating ideas through symbols and characters that may not correspond directly to spoken sounds.
Ancient scripts are tangible evidence of past events and beliefs, offering insights into ancient societies’ rituals, philosophies, and intellectual life.
Unlike spoken language, which is ephemeral, scripts provide a visual medium, employing ideograms and pictograms to convey complex information and ideas beyond the world of speech.
This visual aspect makes ancient scripts a unique and crucial window into our ancestors’ worldviews and narratives, distinct from the transient nature of spoken words.
Uses of Ancient Scripts
Exploring ancient scripts reveals their pivotal roles in various dimensions of civilization. They weren’t merely communication tools but also the backbone that anchored ancient societies’ structure. Their applications spanned numerous domains, each with a unique intrigue.
- Legal and Administrative Uses: Ancient scripts documented laws, transactions, and administrative records, such as Hammurabi’s Code, which was etched in Akkadian on a stone stele. These scripts were essential for the stability and management of societies and were used in business, taxation, and census data.
- Religious Practices: Scripts played a crucial role in religious and ceremonial contexts, preserving rituals, prayers, and sacred texts across generations. Examples include the Vedas in Sanskrit and Egyptian hieroglyphs in religious texts, often accessible only to a select few, creating a priestly class.
- Art and Architecture: Beyond practical uses, ancient scripts adorned buildings, statues, and murals, embedding cultural narratives into art and architecture. Mayan temples and Egyptian pyramids, decorated with respective scripts, serve as historical narrations of their civilizations.
In summary, ancient scripts were multifaceted tools of expression, governance, spirituality, and art, vital to the structure and identity of ancient societies.
In essence, these ancient scripts were the voices of their time, channels through which societies expressed, recorded, and passed down their beliefs, laws, and stories. They acted as the unseen threads weaving together the fabric of their civilization, shaping their identity and culture.
Why are Ancient Scripts Important?
Ancient scripts are crucial for several reasons:
- Window to the Past: Ancient societies’ hieroglyphs and Mayan scripts offer direct insights into their lives, beliefs, and expressions, acting as a bridge to our ancestors. For example, Egyptian Hieroglyphs and Mayan scripts reveal their respective civilizations’ religious beliefs and astronomical knowledge.
- Foundation of Modern Language: Understanding ancient scripts helps appreciate the evolution of modern languages. This exploration traces Sanskrit, Greek, and Latin influences on words, syntax, and grammar back to millennia and highlights the interconnected development of languages.
- Cultural and Historical Understanding: Studying these scripts enriches our comprehension of the world’s cultural diversity and history, promoting a deeper respect for different cultures. For instance, the Cuneiform script of Mesopotamia and the ancient Chinese script offer insights into some of the earliest human civilizations.
In summary, ancient scripts are not just relics of the past but vital keys to understanding human history, language evolution, and the interconnectedness of cultures.
History and Origin Ancient Scripts
Ancient scripts’ journey is a testament to human civilization’s evolution. They mark the transition from prehistoric nonverbal communication to the complex writing systems that laid the foundations for modern languages. The history of these scripts is intertwined with the rise and fall of empires, the spread of cultures, and the human quest for knowledge and expression.
Ancient scripts emerged independently worldwide, with the earliest forms of writing appearing in Mesopotamia, Egypt, China, and Mesoamerica. These early scripts were primarily used for record-keeping, religious texts, and commemorating significant events. Over centuries, they evolved in complexity and style, influenced by the needs of the societies they served.
The development of writing marked a pivotal point in human history. It enabled the preservation of knowledge, culture, and legal systems. It facilitated the administration of vast empires, codifying laws, and disseminating religious doctrine.
The invention of the alphabet, a significant milestone, simplified writing and made it more accessible, ultimately leading to the diverse linguistic landscape of the modern world.
Origin of Ancient Scripts
The origin of ancient scripts is a fascinating story of innovation and adaptation. The earliest known writing system, cuneiform, originated in Mesopotamia around 3200 BC. The Sumerians developed this script, which initially consisted of pictographs and later evolved into a series of wedge-shaped marks impressed onto clay tablets.
Hieroglyphs were developed around the same time in Egypt for religious inscriptions and administrative purposes. These pictorial symbols adorned temple walls and papyrus scrolls, serving as an art form and a means of communication.
The Chinese script, developed around 1200 BC, began as oracle bone inscriptions and evolved into a complex system of logographs, each representing a word or concept. This script laid the groundwork for the Chinese writing system, which remains in use today.
In the Americas, the Mayan script emerged as one of the most sophisticated writing systems of the pre-Columbian era, with its unique combination of syllabic and logographic elements.
These ancient scripts’ origins were shaped by the needs of their respective societies, whether for administrative efficiency, religious expression, or cultural preservation. Each script reflects its creators’ ingenuity and understanding of the world around them, offering invaluable insights into the civilizations that developed it.
Meaning and Symbolism in Ancient Scripts
Decoding the Past
The allure of ancient scripts extends far beyond their functional role as communication tools. Embedded within these venerable symbols are layers of meaning and symbolism, reflecting the beliefs, values, and cosmic understandings of the cultures that created them.
Hieroglyphs
More Than Meets the Eye
Egyptian hieroglyphs are a prime example of a script laden with symbolic meaning. Each hieroglyph was a phonetic symbol or logogram and carried specific connotations. Animals, objects, and gods represented in hieroglyphs were believed to possess divine power.
The ankh symbol, representing life, and the scarab beetle, symbolizing rebirth and the sun’s cycle, are emblematic of how hieroglyphs served dual purposes of communication and spiritual significance.
Cuneiform
Symbols of Power and Divinity
In Mesopotamian societies, the cuneiform script was believed to be a gift from the gods, particularly Enki, who was associated with wisdom and water.
Writing was considered an act of divine creation, mirroring the gods’ ability to shape reality. This belief underscored the power held by scribes and the written word, which was used not only for mundane records but also for incantations and prayers, aiming to bridge the human and divine worlds.
Mayan Glyphs
Calendars and Cosmology
The Mayan script offers profound insights into the Mayans’ complex understanding of time and cosmology. Mayan glyphs represent day names, month names, and Long Count calendar dates, reflecting a sophisticated timekeeping system and a profoundly cyclical view of existence.
These symbols were not merely practical but also deeply imbued with symbolic meaning. They related to deities, natural phenomena, and the cosmos, serving as a narrative of the Mayan worldview.
Phoenician Alphabet
The Spread of Knowledge
While the Phoenician alphabet might seem more utilitarian than pictographic or logographic systems, its simplicity and effectiveness carried their form of symbolism.
By democratizing writing—making it accessible to traders and the wider populace—the Phoenicians symbolized the spread of knowledge and culture. The alphabet became a symbol of connectivity and cultural exchange across the Mediterranean.
Brahmi
The Spiritual Script
The Brahmi script, associated with the edicts of Ashoka, is steeped in Buddhist and Hindu symbolism. The choice to inscribe edicts on pillars and rocks across the landscape symbolized the unifying power of the emperor’s message and its eternal nature, akin to the eternal truths of the religions it often expressed. The script became a symbol of moral and spiritual authority, aiming to guide the moral conduct of the populace.
Linear B
A Window into Mycenaean Society
The decipherment of Linear B tablets revealed a wealth of information about Mycenaean society, including its religious practices and economic organization.
While primarily for record-keeping, the symbols used in Linear B offer indirect symbolism through their depiction of deities, commodities, and administrative roles. They portray a society deeply reliant on and respecting its gods and natural resources.
Ogham
The Sacred Groves
Ogham’s use, primarily on standing stones in landscapes of spiritual significance, underscores its symbolic role as a mediator between the earthly and the divine. The simplicity of the script, combined with its natural medium—stone or wood—symbolizes a profound connection to nature and the ancestral, possibly serving as a territorial claim or a memorial that linked the present with the ancestral past.
In essence, ancient scripts served as more than mere conveyors of information; they were carriers of cultural identity, cosmic knowledge, and spiritual beliefs.
Studying these scripts and their inherent symbolism offers invaluable insights into ancient civilizations’ intellectual and spiritual landscapes. It reveals the universal human endeavor to find meaning and order in the cosmos through the power of the written word.
Ancient Scripts in Popular Culture
Ancient scripts frequently intrigue and inspire elements of modern popular culture, from movies to video games, literature, and beyond. These historical symbols add layers of mystery and authenticity, captivating audiences worldwide.
- Movies and TV: Films and series use ancient scripts as plot devices, transforming Egyptian hieroglyphs or Norse runes into keys unlocking adventures and mysteries.
- Video Games: Players encounter ancient scripts as puzzles or magical incantations, immersing themselves in worlds woven from history and myth.
- Literature: Authors weave these scripts into narratives, where deciphering a script might unveil secrets spanning cultures and epochs.
- Art and Design: The aesthetic allure of ancient scripts embellishes modern fashion, artwork, and digital designs, blending antiquity with contemporary style.
- Social Media: Platforms like Instagram and YouTube spread knowledge and fascination with ancient scripts, making antiquity accessible and engaging.
In sum, ancient scripts bridge the past and present, enriching popular culture with their enduring mystery and beauty.
Usage In Everyday Life
Ancient scripts subtly integrate into our daily lives, appearing in tattoos, jewelry, and architecture. They offer unique connections to the past and personal expression.
- Tattoos: Many choose tattoos featuring ancient scripts like Sanskrit, classical Greek, or Egyptian hieroglyphs. These tattoos go beyond aesthetics and symbolize the wearer’s identity, beliefs, and personal stories.
- Jewelry: Jewelry often bears ancient scripts, from Egyptian hieroglyph-engraved pendants to Celtic rune rings. These items are more than fashion accessories; they’re wearable pieces of history that evoke ancient cultures and spark conversations about their origins and meanings.
- Architecture: Inscriptions in languages like Latin or ancient Hebrew sometimes feature buildings and public spaces, adding artistic and historical depth. These scripts enhance structures’ aesthetic appeal while narrating stories of historical significance or cultural practices.
In each instance, ancient scripts enrich modern life, adding layers of meaning and connecting individuals to historical traditions and cultural legacies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Some of the Most Challenging Ancient Scripts to Decipher?
The most challenging ancient scripts to decipher include Linear A, Etruscan, Meroitic, and the Indus script. They’re real brain teasers, but don’t let that put you off!
How Have Ancient Scripts Influenced Modern Language?
Ancient scripts have shaped modern language immensely. They’ve provided the foundation for alphabets, syntax, and semantics. Think of them as the roots from which today’s diverse linguistic forest has sprung.
Are There Any Ancient Scripts That Are Still in Use Today?
Yes, ancient scripts are still used today. For example, you’re using the Latin script, which has existed since 700 BC. Chinese and Arabic scripts are also ancient and still in regular use.
What Tools or Techniques Are Commonly Used to Decipher Ancient Scripts?
Deciphering ancient scripts typically involves linguistic analysis, comparative methods, and digital technologies. To cross-reference languages, you’d also need a Rosetta Stone-like artifact. It’s a complex, fascinating process, like solving a historical puzzle.
Have There Been Any Recent Discoveries or Advancements in the Study of Ancient Scripts?
Yes, there have been recent advancements. Modern technology, such as AI, is now being utilized to decipher ancient scripts. This has led to discovering and understanding previously impenetrable scripts, revealing many past secrets.
Last Thoughts
So, you’ve ventured through the captivating world of ancient scripts. You’ve grasped their history, usage, and symbolism. You’ve seen how they’re still pertinent, appearing in popular culture and everyday life.
Remember, these scripts aren’t just artifacts; they’re living connections to our past. Hopefully, you’re now motivated to explore this topic further. Keep investigating because every script has a story to tell.
And who knows? You might just uncover a few mysteries of your own.
Before You Go
We hope you enjoyed this journey through ancient scripts. If you found this guide enlightening, we encourage you to share it with others. Spreading knowledge helps us all better understand our shared history.
Let’s cherish these fascinating connections to our past.
Check Other Ancient Scripts
- Logographic Scripts
- Syllabic Scripts
- Alphabetic Scripts
- Pictographic Scripts
- Abugida Scripts
- Abjads (Consonantal Alphabets)
- Undeciphered Scripts
More on Symbols
History of Symbols: How Ancient Marks Shape Our Modern World!
From Cave Walls to Emojis—A Journey Through Time Have you ever wondered about the history of symbols? Maybe you’ve wondered about their global variations or how they’ve shaped our world. Prepare to have your curiosity …
Check it Out!Tattoos and Their Secret Powers: How Ink Can Change Your Life!
Exploring the Art, Meaning, and Culture of Ink! Are you intrigued by tattoos? Are you curious about the stories they tell and the intricate details they contain? Look no further. You might be wondering about …
Check it Out!Masonic Symbols Unlocked: Discover the Secret Meanings Behind the World’s Most Mysterious Icons!
The Hidden Powers and Ancient Secrets You Never Knew! Are you intrigued by masonic symbols and their profound meanings? Perhaps you’ve seen the square, compasses, or the all-seeing eye and wondered about their significance? Thankfully, …
Check it Out!Military Insignia: Unlock the Hidden Meanings Behind These Powerful Symbols
From Zero to Hero: Uncover How Military Insignia Define Power and Prestige Are you curious about the meaning behind military insignia or rank emblems? Have you ever wondered about their significance or history? This comprehensive …
Check it Out!More Symbols